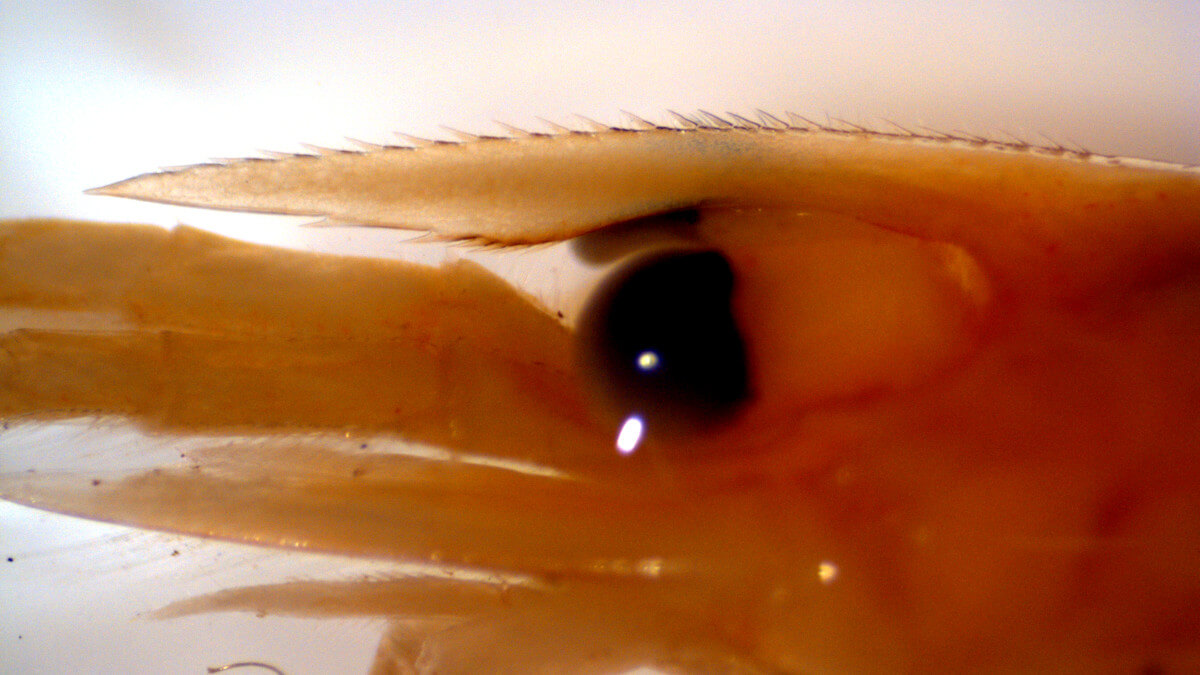
Indistinct river shrimp - Caridina indistincta
This page was created in partnership with the Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development. All images courtesy of the Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development.
Identification
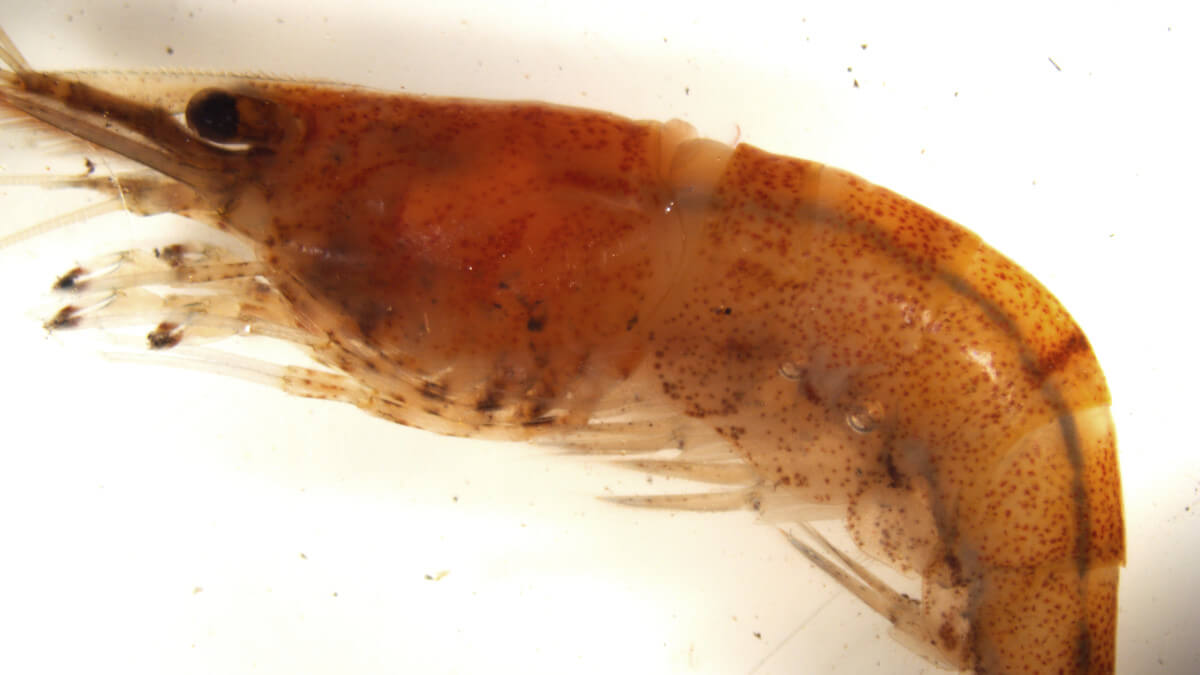
Easily mistaken for the native south-west glass shrimp (Palaemon australis) but can be distinguished by its shorter rostrum, with many more dorsal teeth (upper spines on the rostrum). The indistinct river shrimp is generally smaller than the native glass shrimp and may have faint red speckled pigmentation, while the south-west glass shrimp is more translucent in appearance. Please refer to http://www.fish.wa.gov.au/Documents/biosecurity/freshwater_pest_fact_sheet_indistinct_river_shrimp.pdf for more details.

Caridina indistincta – Note the shorter rostrum (above eye) with many dorsal teeth (upper spines on the rostrum). Image courtesy of Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development.

Palaemon australis – The rostrum (above eye) is longer with fewer dorsal teeth (upper spines on the rostrum). Image courtesy of Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development.
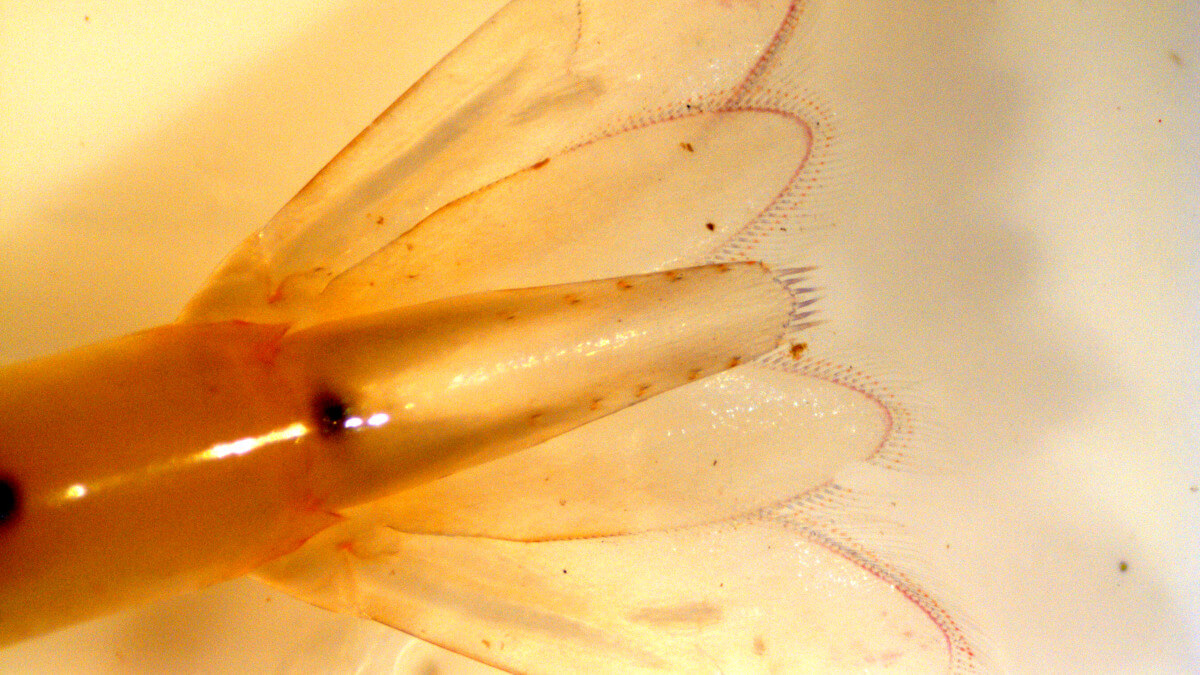
The numbers of spines on the telson (centre section of the tail) is another identifying feature.

5 small spines on telson (centre of tail) of the indistinct river shrimp (Caridina indistincta). Image courtesy of Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development.

2 larger spines on telson (centre of tail) of the native south-west glass shrimp (Palaemon australis). Image courtesy of Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development.
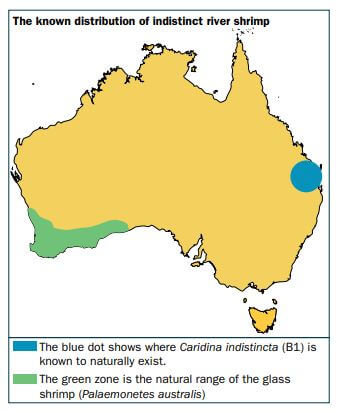
Distribution
A native of South East Queensland (coastal drainage basins), this species has been identified at several locations in south-west Western Australia since 2013, when it was first detected near Perth.
Habitat
The indistinct river shrimp has almost identical environmental preferences to the native south-west glass shrimp, with both favouring fresh to brackish conditions and water temperatures around 20–24°C. Both feed on plant and animal detritus. This overlap of habitat and food sources, as well as life cycle history characteristics, is likely to result in direct competition.
Biology
Although smaller and less robust they are a hardy species that can survive long periods without eating and can spread quickly through flowing waterways. This provides a competitive advantage over the native south-west glass shrimp . Genetic studies have identified at least 5 subspecies of indistinct river shrimp (A-E) that until recently were all thought to be the same species. Specimens collected from WA have been identified as C. indistincta (B1).
Management
Captured individuals should be disposed of humanely (e.g. in an ice slurry). If possible, send the individual along with a photo and location details to the aquatic biosecurity section of the Department of Primary Industry and Regional Development . Please report any suspected aquatic pest species by calling FishWatch hotline (1800 815 507), or via the WA PestWatch website or phone app.
Further information
Please refer to http://www.fish.wa.gov.au/Documents/biosecurity/freshwater_pest_fact_sheet_indistinct_river_shrimp.pdf for more details.